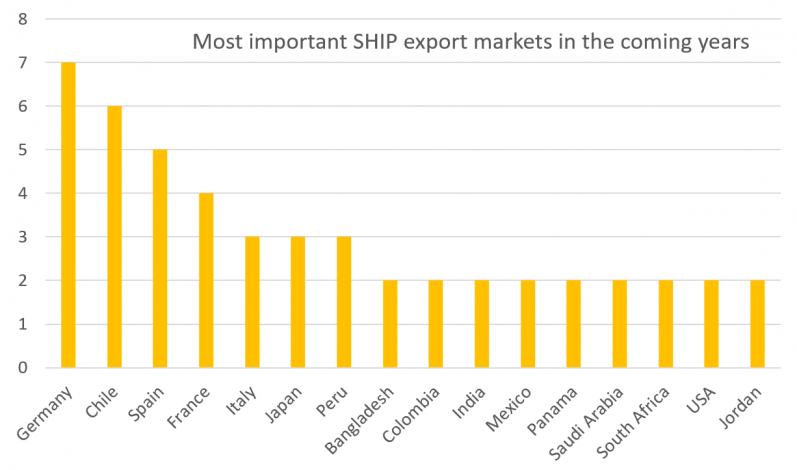
There are opportunities for solar industrial heat in a large number of countries globally. Among the key markets are Germany, Chile, Spain and France, which were named most by turnkey SHIP suppliers when asked for “the three most important SHIP export markets in the coming years”. Additionally, several countries were listed by at least one SHIP technology supplier: Australia, Belgium, Bolivia, Brazil, Canada, China, Costa Rica, Cuba, Cyprus, Indonesia, Namibia, Netherlands, South Korea, Sri Lanka, United Arab Emirates, and Turkey. These results come from the survey carried out in spring 2021 among the around 80 companies listed on the SHIP Supplier World Map, created by the international Solar Payback project.
Source: Solar Payback SHIP supplier survey 2021
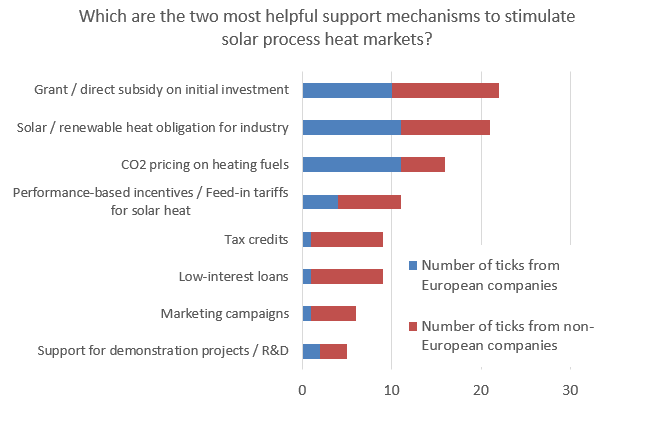
Despite its global potential, SHIP is still a small market. In 2020, only 74 SHIP plants with a combined capacity of 91 MWth (130,745 m2) were commissioned around the world – compared to 86 and 99 systems in 2019 and 2018, respectively. Hence, support schemes are absolutely necessary to increase the deployment rates. Little has been analysed so far as to which support measures are suitable for stimulating SHIP markets. In the above mentioned survey in May 2021, the technology suppliers selected two options from a list of eight measures that they found “most helpful for stimulating solar process heat demand”.
Assessment of support schemes by SHIP technology suppliers from Europe marked blue, from outside Europe marked red (50 answers)
Source: Solar Payback SHIP supplier survey 2021
CO2 pricing creates a level playing field for solar heat
Direct investment grants are as popular among SHIP technology suppliers as solar heat obligations. Both options where ticked more than 20 times by the around 50 SHIP suppliers that participated in the survey. There is a clear connection between the key export markets and the assessment of the most helpful support schemes in the sense that all the key export markets already offer investment subsidies. They are currently the most used scheme for SHIP, with programmes in Germany, France, Austria, Spain, Italy and China, whereas renewable heat obligations for industry have been in discussion in some countries such as India, but they have not yet been implemented anywhere. “Making SHIP systems mandatory to meet some heat load would be the best possible step”, commented a participant from India, for example.
The answers from European and non-European technology suppliers are balanced in relation to these two measures in positions one and two in the ranking of the most helpful support measures. It is noticeable, however, that CO2 pricing – in third place – was selected even more often by Europe-based suppliers than investment grants. The reason for this choice is obvious. CO2 prices monetize the environmental impact of fossil fuels and allow solar to compete with them in equal terms. This strategy has also found supporters in Latin America already, such as a technology supplier from Mexico, who explained in the questionnaire: “Costs on fuels will incentivize the search for options; obligations from regulators for solar heat will provide a path for that search.”
As expected tax credits and low-interest loans (positions five and six in the ranking) were chosen more often by industry players from outside Europe. What is surprising, however, is that performance-based incentives now also have a good position with solar thermal providers outside of Europe.
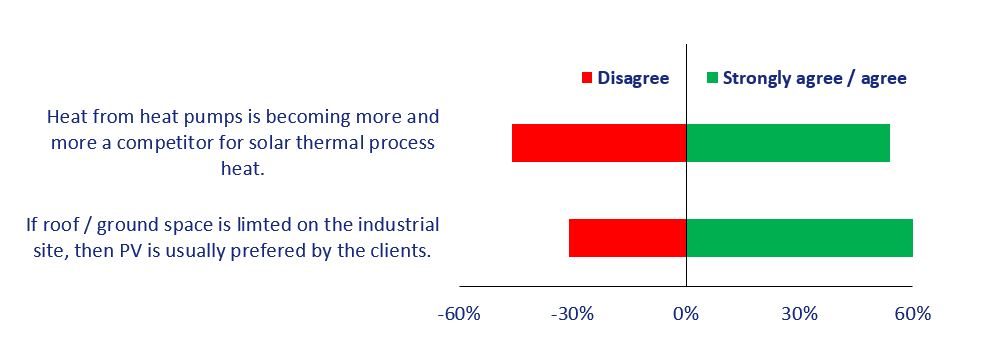
Dissent about heat pump competition
Another important aspect that was queried in the survey was the attitude towards competing technologies like heat pumps and photovoltaics. The following figure shows that more than 50 % of the participating companies agreed that PV and heat pumps are competitors to solar process heat systems. But with heat pumps the picture is more diverse, as 46 % of the companies disagree with this statement. These dissenting voices either came from countries like Mexico, where heat pumps are not common for heat generation in industry yet, or they came from SHIP technology suppliers who consider a combination of heat pumps and solar thermal a suitable solution to offer manufacturers renewable heat.
Around 50 SHIP technology suppliers evaluated these two statements in the survey in April/May 2021
Organisations mentioned in this article:
More data from the analysis was already published in two news items in April/May 2021: